Leetcode347:前K个高频元素——优先队列、堆
题目
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/
从这题开始学会使用堆
题解
堆(heap)
大顶堆:父节点的值大于子节点的值。
小顶堆:父节点的值小于子节点的值。
性质:根节点一定是最大(最小)值
这是一个小顶堆的例子:
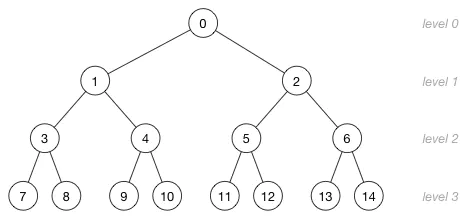
小顶堆例子
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wmyskxz/p/9301021.html
ps:会有人把上学期刚学的东西忘得一干二净吗?会,是谁我不说😂。
优先队列(priority_queue)
优先队列具有队列的所有特性,包括基本操作,只是在这基础上添加了内部的一个排序,它本质是一个堆实现的。
直接看c++ STL
头文件: #include<queue>
定义:priority_queue<int> p; 默认为大顶堆
或priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional> Type为数据类型, Container为保存数据的容器,Functional为元素比较方式。
如priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, decltype(&cmp)> q(cmp);
其中比较函数为:
static bool cmp(pair<int, int>& m, pair<int, int>& n) {
return m.second > n.second;
}
这里定义的是一个储存pair<int,int>的小顶堆。
操作(和队列基本操作相同:
- top 访问队头元素
- empty 队列是否为空
- size 返回队列内元素个数
- push 插入元素到队尾 (并排序)
- emplace 原地构造一个元素并插入队列
- pop 弹出队头元素
- swap 交换内容
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36888577/article/details/79937886
排序大法和大顶堆法
先搞清楚这些咱们才开始做题:
首先最容易想到的,就是统计次数,时间复杂度O(n)。再排序,时间复杂度O(nlogn)。总时间复杂度O(nlogn)
下面是自己写的代码:
class Solution:
def topKFrequent(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
s = {}
for i in nums:
if i not in s.keys():
s[i] = 1
else:
s[i] += 1
s1 = [(a,b) for a,b in s.items()]
s2 = sorted(s1, key=lambda x:x[1], reverse=True)
print(s2)
return [s2[i][0] for i in range(k)]
同样的,如果用大顶堆把所有[数字,出现次数]加入进去,然后k次返回堆顶元素,时间复杂度也是O(nlogn)。涉及到数据结构的话,最好还是用c艹来写:
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(pair<int,int>&m, pair<int,int>&n){
return m.second < n.second;
}
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int,int> occur;
for( auto& v:nums){
occur[v]++;
}
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,decltype(&cmp)> q(cmp);
for(auto& [num,count]:occur){
q.emplace(num,count);
}
vector<int> res;
while(k>0){
res.push_back(q.top().first);
q.pop();
k--;
}
return res;
}
};
以上两种方法时间复杂度为O(nlogn),都不符合题目要求。那么要做到“优于O(nlogn)”用什么方法呢?
小顶堆法
取自官方题解:
在这里,我们可以利用堆的思想:建立一个小顶堆,然后遍历「出现次数数组」:
- 如果堆的元素个数小于 k,就可以直接插入堆中。
- 如果堆的元素个数等于 k,则检查堆顶与当前出现次数的大小。如果堆顶更大,说明至少有 k 个数字的出现次数比当前值大,故舍弃当前值;否则,就弹出堆顶,并将当前值插入堆中。
遍历完成后,堆中的元素就代表了「出现次数数组」中前 k 大的值。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(pair<int, int>& m, pair<int, int>& n) {
return m.second > n.second;
}
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int, int> occurrences;
for (auto& v : nums) {
occurrences[v]++;
}
// pair 的第一个元素代表数组的值,第二个元素代表了该值出现的次数
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, decltype(&cmp)> q(cmp);
for (auto& [num, count] : occurrences) {
if (q.size() == k) {
if (q.top().second < count) {
q.pop();
q.emplace(num, count);
}
} else {
q.emplace(num, count);
}
}
vector<int> ret;
while (!q.empty()) {
ret.emplace_back(q.top().first);
q.pop();
}
return ret;
}
};
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/solution/qian-k-ge-gao-pin-yuan-su-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
由于只需要维护大小为k的堆,所以空间复杂度会小。而且不用对于所有的元素都执行插入堆的操作,所以时间复杂度也优于上面的方法。